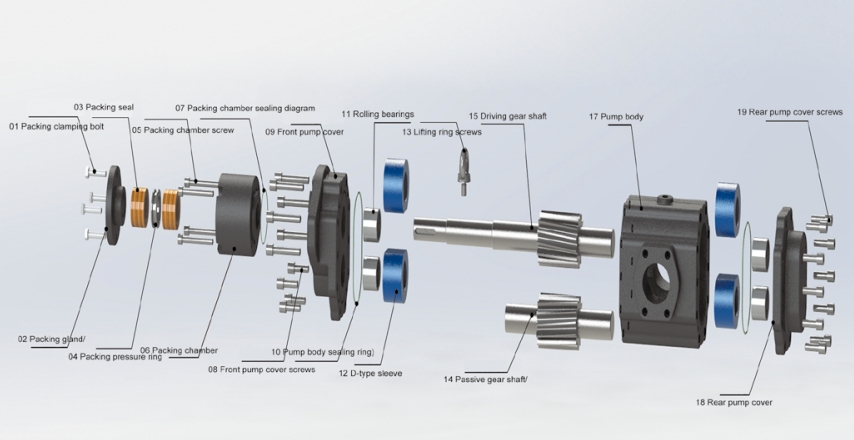
Let’s first discuss the types of gear pumps. Here, we’ll simply categorize them into spur gear pumps and helical gear pumps.
Advantages of Helical Gear Pumps
- Smooth Operation and Low Noise: This is the most prominent advantage of helical gear pumps. When helical gears mesh, their tooth surfaces gradually engage and disengage, rather than engaging and disengaging across their entire width like spur gears. This “gradual” engagement significantly reduces shock, vibration, and the resulting noise.
- Low Flow Pulsation and Stable Output: Because a greater number of tooth pairs engage simultaneously (a larger overlap coefficient), flow delivery is more continuous. This results in significantly lower instantaneous flow pulsation than with spur gear pumps, reducing pressure pulsation in the hydraulic system and improving system stability and component life.
- Higher Volumetric Efficiency: The tooth profile of helical gears creates a longer and more tortuous leakage path through the end clearance, resulting in relatively less internal leakage under high-pressure conditions. Therefore, volumetric efficiency is generally higher than that of spur gear pumps of the same specifications. Disadvantages of Helical Gear Pumps
- Axial Force: The helix angle of the gears generates a force (axial force) along the gear axis during operation. This force must be balanced by bearings capable of withstanding axial loads, such as angular contact ball bearings, which increases bearing complexity and cost.
- Complex Manufacturing and Assembly: Helical gears require higher machining precision, and the axial positioning of the gear shaft in the pump body must be extremely precise to ensure the proper clearance between the gear end face and the pump cover. Assembly is also more complex than with spur gear pumps.
- Higher Cost: Due to the difficulty of machining and the cost of components such as bearings, helical gear pumps are generally more expensive to manufacture than spur gear pumps.
Advantages of Spur Gear Pumps
- Simple Structure and Low Cost: The absence of axial force allows the use of simple deep groove ball bearings; the gears are also easy to machine. This results in competitive manufacturing and maintenance costs.
- Durable and Impact-Resistant: The simple structure means high reliability and greater adaptability to harsh operating conditions. Disadvantages of Spur Gear Pumps
- Severe Oil Trapping: The inherent oil trapping problem inherent in gear pumps (oil trapped in the enclosed volume formed by the two pairs of gear teeth and the pump casing) is more pronounced in spur gear pumps. While unloading slots can alleviate this problem, it remains a major source of noise and vibration.
- Large Flow and Pressure Pulsations: Output instability affects the stability of the entire hydraulic system.
- High Noise: This is a major limitation for its use in demanding environments.
The comparison of the noise, pulsation, and volumetric efficiency graphs below clearly illustrates this.
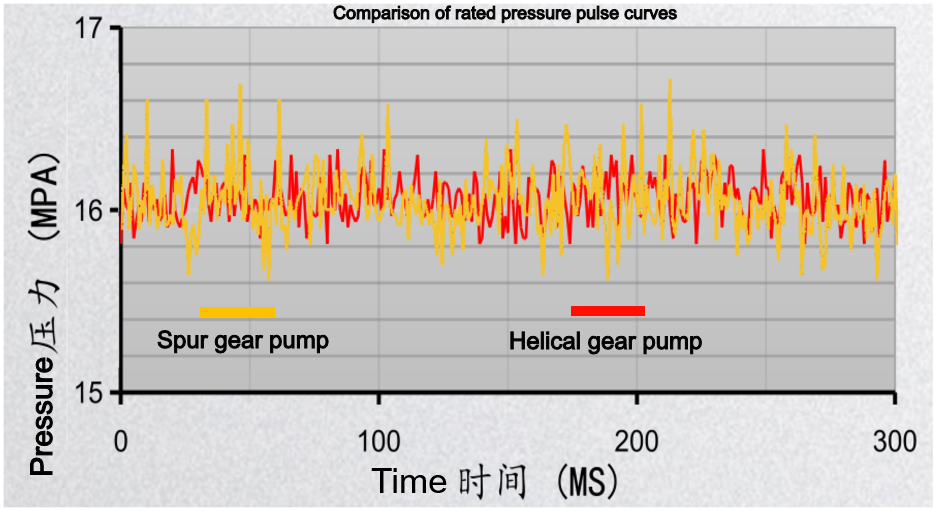
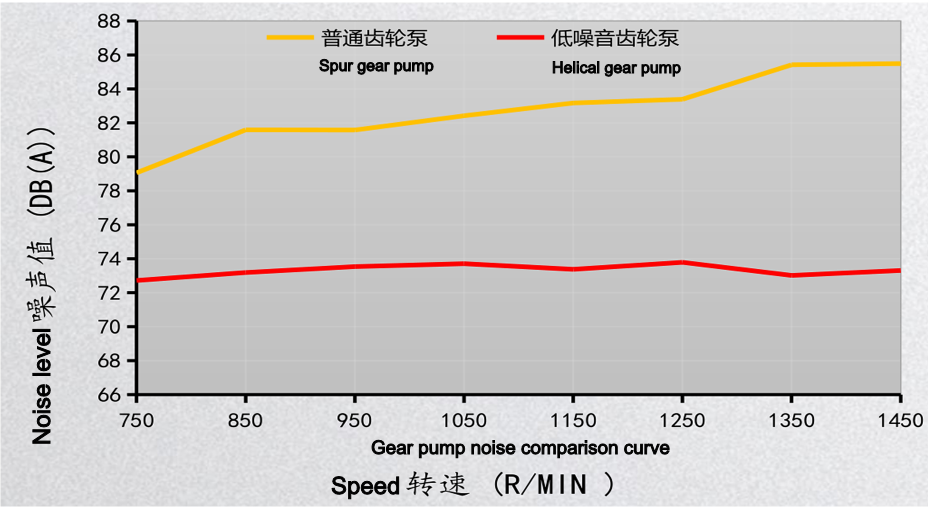
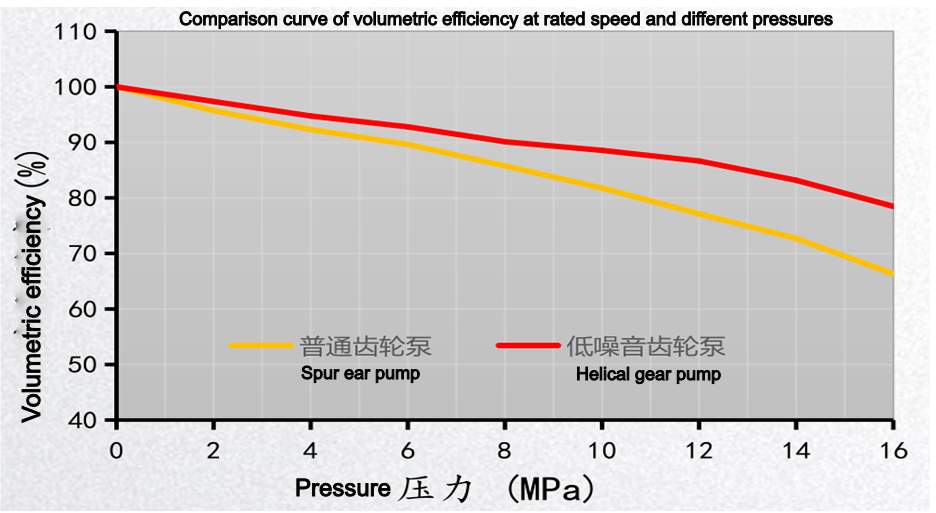
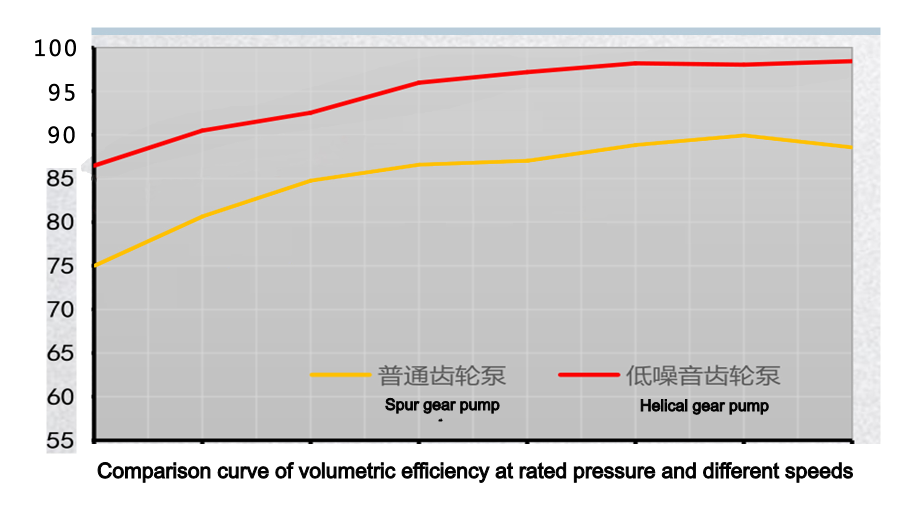
Comparisons yield selection recommendations.
Choose a spur gear pump if your application is noise-insensitive, budget-constrained, and operating under general conditions. For example, in agricultural machinery, simple lubrication and oil supply systems, or low-speed conveying applications, a spur gear pump’s ruggedness and low cost make it a good choice.
Choose a helical gear pump if your application requires high noise, vibration, and flow stability. For example, in passenger car or aircraft engine and transmission hydraulic systems, chemical precision batching equipment, or any other advanced industrial equipment requiring quiet and smooth operation, the helical gear pump’s multiple performance advantages more than offset its slightly higher cost and complexity.